Did you know that female pitbulls can stay in heat for up to 21 days? That’s almost three weeks of hormonal changes and potential mating opportunities. During this time, pitbulls may exhibit physical and behavioral changes, such as swelling of the vulva, increased urination, and a heightened interest in male dogs. It’s important for owners to be aware of this cycle and take necessary precautions to prevent unwanted pregnancies or manage their dog’s behavior during this time.
Understanding the duration of a pitbull’s heat cycle is crucial for responsible pet ownership. The average heat cycle for a female pitbull lasts around 18 to 21 days, with individual variations. This cycle consists of four stages: proestrus, estrus, diestrus, and anestrus. During the proestrus stage, the female may experience vaginal bleeding and attract male dogs, but she is not yet ready for mating. The estrus stage follows, where the female is receptive to breeding. It’s essential to keep female pitbulls confined or supervised during this time to prevent unwanted pregnancies. By being knowledgeable about the duration and stages of a pitbull’s heat cycle, owners can ensure the well-being and safety of their pets.
:strip_icc()/heat-cycle-for-dogs-3385378_FINAL-resized-16b20c1a5ae146e4a23c6660ff2612e7.png)
How Long Does a Pitbull Stay in Heat?
Understanding the Heat Cycle of Pitbulls
The heat cycle, also known as estrus, is the reproductive cycle of female dogs. For pitbulls, the length of their heat cycle can vary, but on average, it lasts about 2 to 3 weeks. The cycle is divided into different stages: proestrus, estrus, and diestrus. During proestrus, which lasts around 7 to 10 days, the female pitbull shows signs of swelling, discharge, and increased urination. This is the period when male dogs are attracted to her but she is not ready to mate yet. Next comes the estrus stage, which typically lasts for about 7 to 10 days. This is when the female is fertile and receptive to mating. Finally, diestrus is the period where the female is no longer receptive and her reproductive system returns to its normal state. The length of each stage may vary between individual dogs and can be influenced by factors such as age and hormonal balance. It is essential to keep an eye on the specific signs and behavior of your pitbull during their heat cycle to ensure their health and well-being.
Signs and Symptoms of a Pitbull in Heat
When a pitbull enters the heat cycle, there are several noticeable signs and symptoms to be aware of. One of the most prominent signs is swelling of the vulva, which indicates that the dog is entering proestrus. This swelling can be quite noticeable and may last for a few days. Additionally, female pitbulls in heat may experience a bloody discharge, which is a normal part of the reproductive process. This discharge is often a light red color, resembling diluted blood. Another sign to look out for is behavioral changes. During the estrus stage, the female pitbull may become more receptive to male dogs and exhibit flirtatious behavior. The dog’s behavior may change from being aloof to actively seeking attention and approach from male dogs. It is important to note that during this period, female pitbulls should be kept away from intact males to avoid an unintentional mating.
Dealing with a Pitbull in Heat
When your pitbull is in heat, there are certain precautions and measures to take to ensure her safety and prevent unwanted pregnancies. First and foremost, it is crucial to keep your female pitbull indoors or in a securely fenced area to prevent her from escaping and mating with male dogs. During the heat cycle, she may be more inclined to roam and search for a mate. It is also a good idea to avoid taking her on walks or to public places where intact males may be present. This will help reduce the chances of unwanted attention and potential aggression from other dogs. Proper hygiene is essential during this time. Make sure to clean your pitbull’s genital area regularly to keep her comfortable and prevent any infections. It is also a good practice to use doggy diapers or disposable panties to contain any discharge and avoid staining furniture or carpets. Lastly, if you do not plan on breeding your pitbull, it is highly advisable to have her spayed to prevent future heats and the associated challenges.
The Importance of Spaying and Neutering
Benefits of Spaying and Neutering Pitbulls
Spaying or neutering your pitbull has numerous benefits, both for their individual health and the overall canine population. By spaying your female pitbull, you eliminate the risk of unwanted pregnancies, reducing the number of homeless dogs. This, in turn, helps alleviate the strain on animal shelters and rescues. Spaying also eliminates the potential for certain reproductive diseases, such as uterine infections and mammary tumors. Neutering male pitbulls can also have various advantages. It helps prevent testicular cancer and reduces the risk of prostate problems. It can also mitigate certain behavioral issues, such as territorial marking and aggression. Overall, spaying and neutering are important steps in responsible pet ownership and contribute to the long-term welfare of pitbulls and the canine community as a whole.
Spaying and Neutering Pitbulls: The Procedure and Aftercare
Spaying and neutering procedures for pitbulls are typically performed by veterinarians and involve the permanent removal of the reproductive organs. Spaying, also known as an ovariohysterectomy, involves removing the ovaries and the uterus. Neutering, or castration, involves the removal of the testicles in male dogs. Both procedures are performed under anesthesia, ensuring the safety and comfort of the animals. After the surgery, it is crucial to provide proper post-operative care to promote healing and prevent infections. This may involve keeping the incision site clean and dry, administering any prescribed pain medications or antibiotics, and limiting physical activity for a few days to allow for recovery. Your veterinarian will provide specific instructions tailored to your pitbull’s needs. It is important to follow these guidelines to ensure a smooth and successful recovery.
The Importance of Early Spaying and Neutering
Early spaying and neutering have several advantages for pitbulls and other dog breeds. The procedure can typically be performed as early as 8 weeks of age. Spaying female pitbulls before their first heat cycle greatly reduces the risk of mammary tumors, which are commonly found in unspayed females. Early neutering male pitbulls can help prevent behavioral issues associated with intact males, such as aggressive and dominant behavior. Additionally, spaying or neutering at an early age eliminates the possibility of accidental litters if your pitbull encounters an intact dog before being spayed or neutered. It is important to consult with your veterinarian to determine the best time for spaying or neutering your pitbull, taking into consideration their overall health and development.
The Pros and Cons of Spaying and Neutering Pitbulls
Benefits of Spaying and Neutering Pitbulls
1. Population Control: By spaying or neutering your pitbull, you contribute to reducing the number of homeless and unwanted dogs.
2. Health Benefits: Spaying reduces the risk of uterine infections and mammary tumors in female pitbulls, while neutering reduces the risk of testicular cancer and prostate problems in males.
3. Behavioral Improvements: Neutering male pitbulls can often help alleviate certain behavioral issues, such as marking territory and aggression.
4. Reduced Roaming Tendencies: Unaltered pitbulls are more likely to roam in search of a mate. Spaying or neutering can reduce this urge, keeping your pet safer and closer to home.
5. Fewer Unwanted Pregnancies: Spaying prevents unwanted pregnancies and reduces the chances of breeding-related complications for female pitbulls.
Potential Drawbacks of Spaying and Neutering Pitbulls
1. Surgical Risks: Like any surgery, spaying or neutering carries a small risk of complications and adverse reactions to anesthesia.
2. Hormonal Changes: Spaying or neutering can lead to hormonal changes in pitbulls, potentially affecting their metabolism and behavior.
3. Increased Risk of Certain Orthopedic Conditions: Some studies suggest that early spaying or neutering may increase the risk of certain orthopedic conditions, such as hip dysplasia and cruciate ligament injuries.
4. Impact on Appearance: Neutering male pitbulls can result in changes to their physical appearance, including reduced muscle development and a less masculine appearance.
5. Limited Breeding Options: Once your pitbull is spayed or neutered, they can no longer reproduce, limiting your options if you decide to breed them in the future.
How to Care for a Pitbull in Heat
Tips for Caring for Your Pitbull During Her Heat Cycle
1. Keep Her Indoors or Securely Fenced: To prevent unplanned matings and potential escape attempts, make sure your pitbull is kept indoors or in a securely fenced area.
2. Provide Extra Cleanliness: Regularly clean your pitbull’s genital area to prevent discomfort and the risk of infections. Consider using doggy diapers or disposable panties to contain any discharge.
3. Avoid Public Places: During the heat cycle, avoid taking your pitbull on walks or to public places where intact males may be present. This helps minimize unwanted attention and potential conflicts with other dogs.
4. Offer Distractions and Enrichment: Increase mental and physical stimulation for your pitbull during her heat cycle. Engage her in interactive play, provide puzzle toys, and offer training sessions to keep her engaged and distracted from male dogs.
5. Consider Hormonal Options: Talk to your veterinarian about hormonal options such as medications or injections to suppress heat cycles if breeding is not a desired outcome for your pitbull.
6. Spay Your Pitbull: If you do not plan on breeding your pitbull, spaying her is the most effective way to manage the heat cycle and prevent future heats and complications.
Understanding the Risks of Breeding Pitbulls
While breeding pitbulls may seem like an exciting prospect, it is crucial to understand the risks and responsibilities that come with it. Breeding pitbulls should only be undertaken by experienced and knowledgeable breeders who have a thorough understanding of genetics, health screenings, and proper care for both the dam and the puppies. Breeding without adequate knowledge and preparation can lead to a myriad of issues, including genetic disorders, health problems, and an increased population of unwanted dogs. It is also important to consider the ethical implications of breeding, ensuring that any breeding is done with the well-being of the dogs in mind rather than for financial gain or personal interest. Responsible breeding practices involve extensive research, health testing, responsible placement of puppies, and a commitment to the long-term welfare and betterment of the breed.
Key Takeaways: How Long Does a Pitbull Stay in Heat?
- A female pitbull is typically in heat for about 2 to 3 weeks.
- The heat cycle of a pitbull consists of different stages: proestrus, estrus, and diestrus.
- During proestrus, the female dog may experience vaginal bleeding and swelling.
- Estrus is the period when the female is receptive to mating.
- Diestrus follows estrus and is the final stage of the heat cycle.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are you curious about the duration of a pitbull’s heat cycle? Look no further! Here are some commonly asked questions answered for you.
1. How often does a pitbull go into heat?
A female pitbull typically goes into heat every six to eight months. This means that she will experience estrus, or the receptive phase of her reproductive cycle, twice a year on average.
However, it’s important to note that the regularity of a pitbull’s heat cycle can vary. Some may experience it more frequently, while others may have longer intervals between heats. It’s essential to track your individual dog’s cycle to understand her unique pattern.
2. How long does a pitbull stay in heat?
A female pitbull usually stays in heat for about two to three weeks. This period consists of different stages, including proestrus, estrus, and diestrus.
During the proestrus stage, which typically lasts for about seven to ten days, you may notice some changes in your dog’s behavior, such as a swollen vulva and the presence of discharge. This is followed by the estrus stage, which lasts for about nine to thirteen days and is the time when your pitbull is most fertile. Finally, diestrus is the phase after estrus when the reproductive cycle starts to come to an end.
3. How can I tell if my pitbull is in heat?
There are several signs that can indicate that your pitbull is in heat. One of the most noticeable signs is swelling of the vulva, which may be accompanied by a bloody discharge. During this time, your dog may also exhibit changes in behavior, such as increased restlessness, frequent urination, and a more receptive attitude towards male dogs.
Keep in mind that each dog is different, and some may not display all these signs. It’s crucial to familiarize yourself with your pitbull’s individual patterns and consult with a veterinarian if you have any concerns or questions.
4. Can I spay my pitbull while she is in heat?
While it is technically possible to spay a pitbull while she is in heat, most veterinarians recommend waiting until the heat cycle is over. This is because the blood-rich uterus during heat increases the risk of bleeding during the surgery.
It is generally recommended to spay your pitbull during the anestrus phase, which is the period when your dog is not in heat. Consulting with your veterinarian will ensure that the timing is appropriate and safe for your pet.
5. How can I manage my pitbull’s heat cycle?
When your pitbull is in heat, it’s essential to take some precautions to manage her cycle. One option is to keep her indoors and away from intact male dogs to prevent unwanted pregnancies. Additionally, you may consider using special doggie diapers or reusable sanitary pants to contain any discharge and keep your environment clean.
It’s also important to provide extra care and attention during this time as your pitbull may experience discomfort and mood changes. Be patient and understanding, and consult with a veterinarian if you have any concerns or need guidance on managing your dog’s heat cycle.
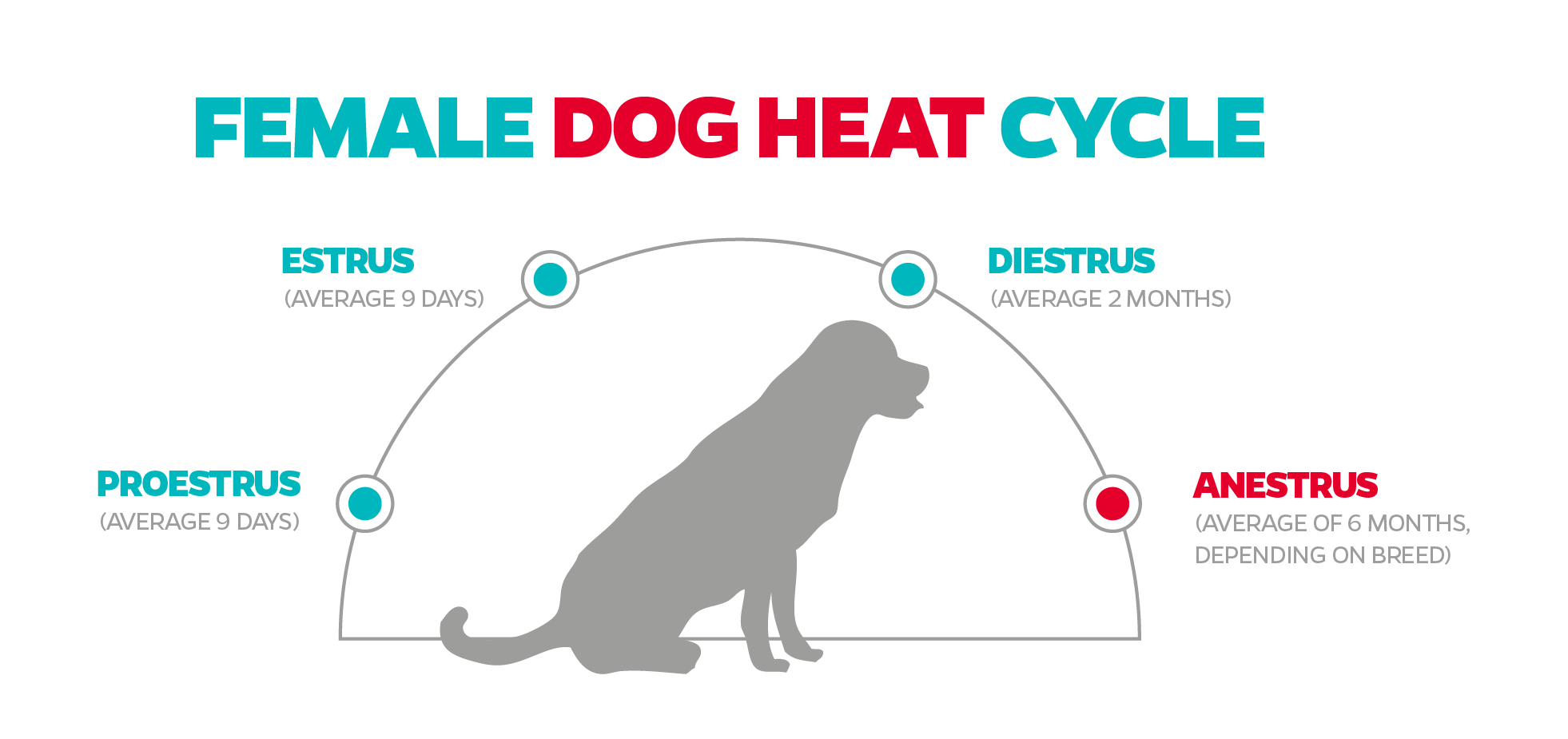
4 Stages of Dog Heat Cycle (may be graphic)
Summary
Pitbulls stay in heat for about 2 to 3 weeks, but it can vary. During this time, they might show certain behaviors like bleeding, swelling, and attracting male dogs. It’s important for owners to understand this natural process and take proper care of their dogs.
It’s crucial to keep your pitbull safe during her heat cycle. Make sure to keep her on a leash when outside to avoid unwanted pregnancies. Also, provide her with extra attention, comfort, and hygiene to help her through this hormonal phase.