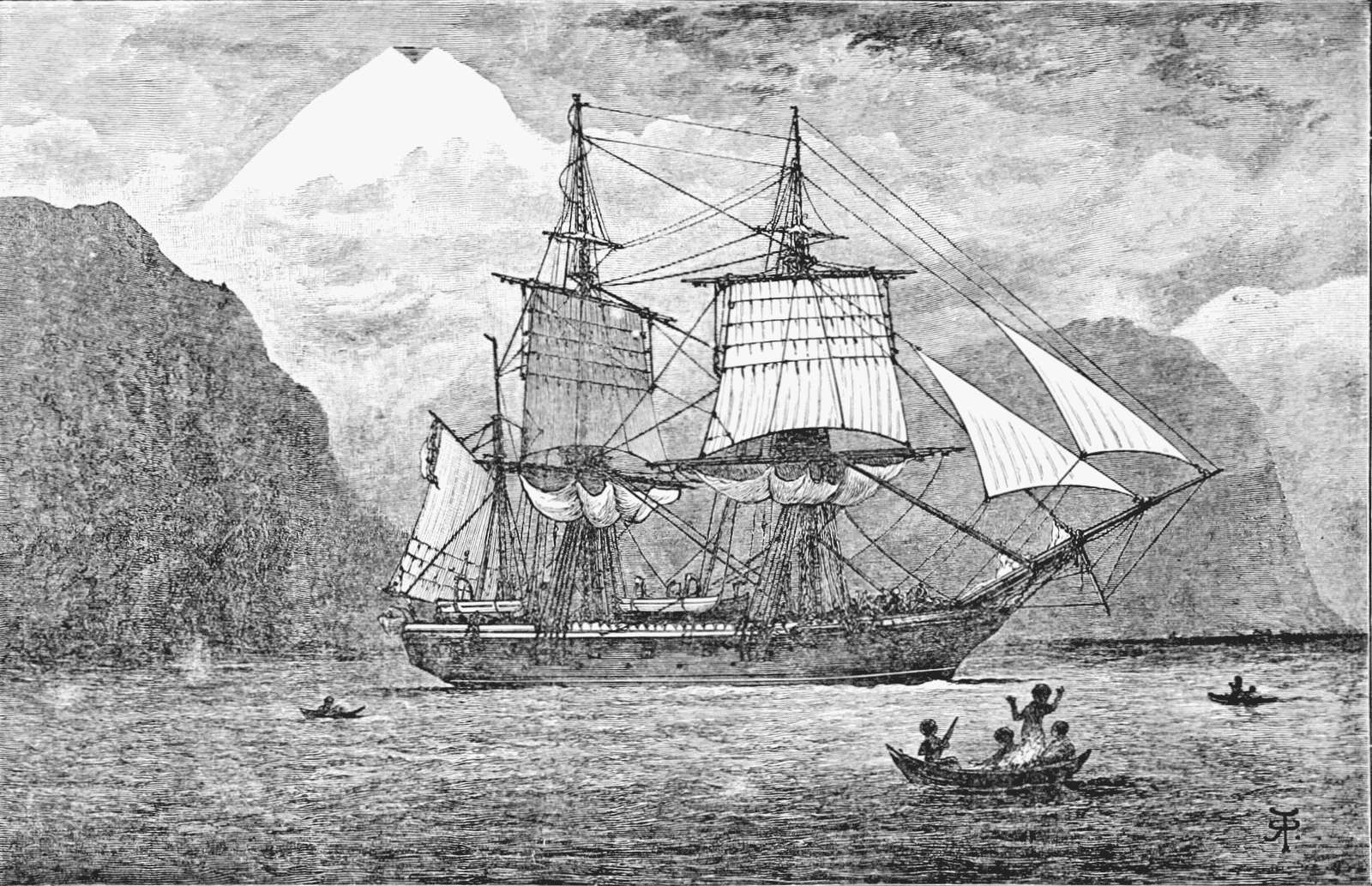Charles Darwin’s job on the Beagle was to serve as the ship’s naturalist, but his work went far beyond simple observation. During his five-year voyage, Darwin collected and documented an extensive array of plant and animal specimens from the places the Beagle visited. This job allowed Darwin to study and gain a deep understanding of the natural world, which eventually led to his groundbreaking theory of evolution.
As the ship’s naturalist, Darwin’s job was to carefully observe and record the different species he encountered, noting their physical characteristics, behaviors, and distribution patterns. He meticulously labeled and cataloged the specimens he collected, creating a valuable collection that would later support his theories. His work on the Beagle laid the foundation for his later concepts of natural selection and the idea that species change over time. Through his extensive observations and analysis, Darwin challenged the prevailing beliefs of his time and revolutionized our understanding of life on Earth.
Charles Darwin’s job on the Beagle was that of a naturalist. He was chosen to be the ship’s onboard scientist and observer, responsible for collecting and documenting various specimens, including plants, animals, and geological samples, during the expedition. Darwin’s job allowed him to closely study diverse ecosystems and species, leading to groundbreaking insights and discoveries that laid the foundation for his theory of evolution.

Charles Darwin’s Role on the Beagle
Charles Darwin, the renowned British naturalist and scientist, is best known for his theory of evolution. However, before he developed this groundbreaking idea, he embarked on a voyage aboard the HMS Beagle that would shape his scientific career. During his time on the Beagle, Darwin had a specific job that contributed to his observations and research. Let’s explore what Charles Darwin’s job was on the Beagle and how it influenced his later scientific discoveries.
1. Naturalist Role
Charles Darwin’s primary role on the Beagle was that of a naturalist. As a naturalist, he was responsible for collecting and studying specimens of plants, animals, and geological formations that he encountered during the voyage. Darwin meticulously observed and documented the characteristics, behaviors, and distribution of various species. This involved collecting specimens, making detailed notes, and sketching illustrations.
His job as a naturalist allowed Darwin to gain a deep understanding of the diversity of life and natural processes. He collected numerous specimens of plants, animals, and fossils from different regions, which later served as evidence for his evolutionary theory. This firsthand experience and collection of data provided a solid foundation for his future scientific research and writings.
Observing Nature’s Patterns
During his time on the Beagle, Darwin became fascinated with the patterns he observed in nature. He noticed that certain species were uniquely adapted to their environments, and that these adaptations were influenced by the characteristics of the habitats. This realization planted the seeds for his theory of natural selection, which would later become the cornerstone of his work on evolution.
Darwin’s job as a naturalist allowed him to witness firsthand the intricate relationships between organisms and their environments. He observed how different species interacted with each other and how they were influenced by ecological factors such as climate, food availability, and competition. These observations formed the basis for his understanding of the interconnectedness of all organisms and the gradual changes that occur over time.
2. Geological Investigations
In addition to his role as a naturalist, Charles Darwin also conducted geological investigations during his time on the Beagle. He studied and collected rock samples, fossils, and geological formations from various locations. Darwin’s observations of the geological features in different regions provided valuable insights into the Earth’s history and supported his ideas about the gradual changes that shape the planet.
Formulating the Theory of Evolution
As Darwin examined the rock layers and fossils he encountered, he noticed patterns that suggested that Earth’s geological history was marked by gradual transformations. This, combined with his observations of diverse species and their adaptations, led him to develop his theory of evolution through natural selection.
Darwin’s geological investigations and observations of living organisms allowed him to piece together a narrative of how life on Earth had changed over time. The physical evidence he gathered provided a temporal framework for his theory, demonstrating that the history of life was not static, but rather a dynamic and continuously evolving process.
3. Collaboration and Contribution
During his time on the Beagle, Charles Darwin collaborated with other scientists and experts. He shared his findings, exchanged ideas, and received guidance from renowned naturalists and geologists. These collaborations provided valuable insights and helped shape Darwin’s thinking as he continued to develop his theories.
John Henslow’s Mentorship
One of the significant collaborations Darwin had during the voyage was with his mentor, John Henslow. Henslow was a professor of botany at the University of Cambridge and played a vital role in shaping Darwin’s scientific career. He provided guidance, introduced Darwin to influential scientific circles, and encouraged him to pursue his interests in natural history.
Henslow’s mentorship was instrumental in Darwin’s growth as a scientist. Their collaboration and discussions laid the groundwork for many of the ideas that would later form the basis of Darwin’s evolutionary theory. Henslow’s influence and support played a crucial role in shaping the direction of Darwin’s career.
Conclusion
Charles Darwin’s job on the Beagle as a naturalist and his geological investigations were fundamental to his scientific journey. The observations and collections he made during the voyage provided a wealth of evidence and insights that contributed to his groundbreaking theory of evolution. Through his role as a naturalist, his geological investigations, and collaborations with fellow scientists, Darwin laid the foundation for modern evolutionary biology and forever changed our understanding of life on Earth.
Key Takeaways: What was Charles Darwin’s job on the Beagle?
- Charles Darwin served as the naturalist on the HMS Beagle.
- His role was to observe and collect various specimens of plants and animals during the voyage.
- Darwin’s job included cataloging and documenting his findings, which would later contribute to his theory of evolution.
- He spent five years exploring the Galapagos Islands, where he made groundbreaking discoveries.
- Darwin’s work on the Beagle laid the foundation for his later revolutionary ideas about the origin of species.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some commonly asked questions about Charles Darwin’s job on the Beagle:
1. What was the purpose of Charles Darwin’s journey on the Beagle?
Charles Darwin’s job on the Beagle was to serve as the ship’s naturalist. The purpose of the journey was to conduct scientific research and collect specimens from various locations around the world. Darwin was responsible for studying and documenting the plants, animals, and geological formations he encountered during the voyage.
His observations and findings during the expedition provided crucial data that later contributed to the development of his theory of evolution by natural selection. Darwin’s role as the naturalist on the Beagle allowed him to gather a wealth of information that shaped his groundbreaking scientific ideas.
2. What specific tasks did Charles Darwin perform on the Beagle?
While on the Beagle, Charles Darwin had several responsibilities. He collected and preserved plant and animal specimens, making detailed notes about their characteristics and habitats. He also conducted geological surveys, examining rock formations and documenting any observations of interest.
In addition, Darwin engaged in regular correspondence with scientists back in England, sharing his findings and discussing his observations. He also had the opportunity to interact with locals in various locations, learning about their cultures and gathering additional information that would contribute to his research.
3. How long did Charles Darwin spend on the Beagle?
Charles Darwin embarked on his journey on the Beagle in December 1831 and returned to England in October 1836. He spent a total of nearly five years aboard the ship, traveling to different parts of the world, including South America, the Galápagos Islands, New Zealand, Australia, and Africa.
During this time, Darwin’s experiences and observations on the Beagle played a crucial role in shaping his scientific thinking and later influenced his groundbreaking work on evolution.
4. Did Charles Darwin publish any works based on his job on the Beagle?
Yes, Charles Darwin published several works based on his job on the Beagle. One of his most famous publications is “The Voyage of the Beagle,” which recounts his experiences, observations, and discoveries during the expedition.
In addition to “The Voyage of the Beagle,” Darwin’s time on the Beagle provided him with valuable insights that eventually led to his seminal work, “On the Origin of Species,” where he presented his theory of evolution.
5. How did Charles Darwin’s job on the Beagle impact his career?
Charles Darwin’s job as the naturalist on the Beagle had a profound impact on his career and the history of science. His observations and collections during the voyage provided crucial evidence for his subsequent scientific theories, most notably the theory of evolution by natural selection.
The knowledge and insights gained from his job on the Beagle propelled Darwin to become one of the most influential scientists of all time. His work revolutionized our understanding of the natural world and continues to be the foundation of modern biology.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/HMS-Beagle-3000-3x2gty-579e23883df78c32765450a0.jpg)
Charles Darwin’s job on the Beagle was to serve as the ship’s naturalist.
His main task was to collect and study specimens of plants, animals, and fossils during the voyage.