As a native of Chihuahua, Mexico, I am often met with surprise when I mention that Chihuahua is actually a desert. Most people associate Chihuahua with its namesake dog breed, but few know about its arid landscape. It’s fascinating how this region, with its rich cultural heritage, has adapted to the challenges of living in a desert environment.
Chihuahua, known as the largest state in Mexico, has a long history intertwined with its desert landscape. This vast and rugged terrain covers approximately 58% of the state and is characterized by its hot and dry climate. With an average rainfall of only about 12 inches per year, the desert poses unique challenges for the people and wildlife that call it home. However, despite the aridity, the region has thrived with its extensive agricultural practices and resourceful use of water. In fact, Chihuahua is known for its extensive irrigation systems that have allowed for successful cultivation of crops like apples, alfalfa, and cotton. This blend of history and adaptability showcases the resilience and ingenuity of both the land and its people in the face of desert conditions.
Is Chihuahua a Desert?
Chihuahua, one of the largest Mexican states, is often associated with deserts due to its arid climate and vast stretches of dry land. In this article, we will explore whether Chihuahua can indeed be classified as a desert. Let’s delve into the geography, climate, and natural features of the region to gain a better understanding.
Geography of Chihuahua
Chihuahua is located in the northern part of Mexico, sharing borders with the United States. It is a landlocked state that spans a diverse range of topographic features. While parts of Chihuahua do consist of desert landscapes, it is important to note that the state is not entirely a desert. The geography of Chihuahua is characterized by a mix of deserts, mountain ranges, canyons, plateaus, and grasslands.
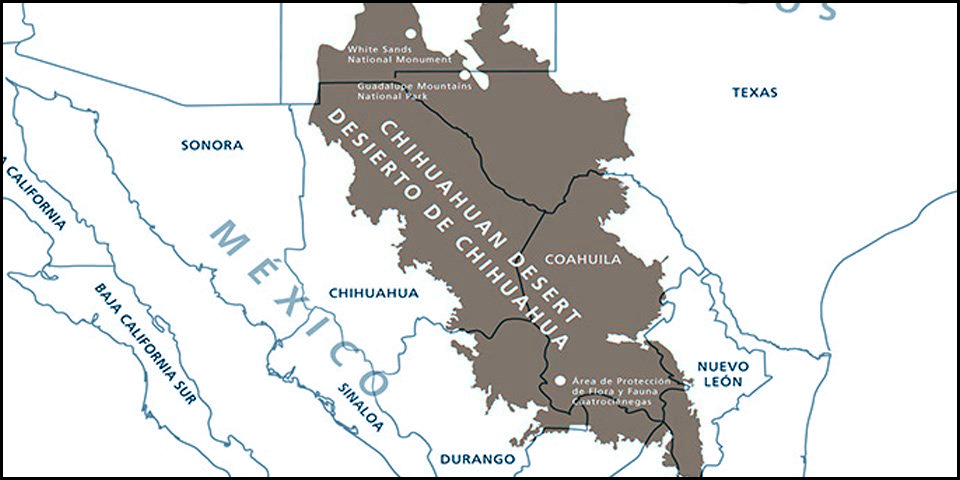
In the western region of Chihuahua, you can find the Chihuahuan Desert, which is the largest desert in North America and stretches across several states. However, as you move towards the east, the landscape changes dramatically, with mountainous terrains dominating the scenery.
In conclusion, while Chihuahua does contain desert regions, it is incorrect to classify the entire state as a desert due to the varied geography that includes mountainous areas, plateaus, canyons, and grasslands.
Climate of Chihuahua
The climate of Chihuahua varies widely across the state, influenced by its diverse geography. Generally, Chihuahua experiences a semi-arid to arid climate, characterized by hot summers and cold winters. Within the state, you can find different climate zones, including steppe, desert, and highland.
In the desert regions of Chihuahua, such as the Chihuahuan Desert, the climate is extremely dry, receiving minimal rainfall throughout the year. These areas have high daytime temperatures that can soar above 100 degrees Fahrenheit (37.8 degrees Celsius). On the other hand, the mountainous regions of Chihuahua experience cooler temperatures due to higher elevations, and snowfall is not uncommon during winters.
Although Chihuahua has significant desert areas, the presence of distinct climate zones within the state further supports the fact that it cannot be classified as an entire desert.
Wildlife in Chihuahua
Chihuahua’s diverse geography and climate create unique ecosystems that support a wide variety of wildlife. In the desert regions, you will find adaptations unique to desert animals such as roadrunners, kangaroo rats, and various species of cacti. The Chihuahuan Desert is also home to several reptile species, including rattlesnakes and lizards.
As you move towards the mountainous areas, the fauna changes, and you can find species like black bears, mountain lions, elk, and various bird species. The Sierra Madre Occidental range, located in the western part of Chihuahua, is a biodiversity hotspot where flora and fauna thrive.
The presence of diverse wildlife in Chihuahua further emphasizes the fact that it is not solely a desert but a region that supports a range of ecosystems.
Impact of Chihuahua’s Geography and Climate
The unique geography and climate of Chihuahua contribute to the region’s ecosystem and have an impact on the people and culture of the state. The desert regions, for example, have influenced the development of a desert-adapted lifestyle for some communities, while the mountainous areas provide opportunities for recreational activities such as hiking and skiing.
Moreover, the diverse geography of Chihuahua also supports various economic activities. In addition to agriculture and livestock farming in the grasslands, Chihuahua is rich in mineral resources, such as copper and silver, found in its mountainous regions.
In conclusion, the geography and climate of Chihuahua not only shape its natural landscapes and wildlife but also play a significant role in the lives of its inhabitants and the economy of the state.
Chihuahua’s Desert Regions: A Closer Look
While it has been established that Chihuahua is not entirely a desert, let’s now take a closer look at the desert regions that can be found within the state. Understanding these unique landscapes will provide a deeper insight into the ecological features of Chihuahua.
The Chihuahuan Desert
The Chihuahuan Desert, located primarily in the states of Chihuahua and Coahuila, is the largest desert in North America, extending into the southern parts of the United States as well. Covering an area of approximately 140,000 square miles (360,000 square kilometers), it showcases the typical desert characteristics of cacti, succulents, and sparse vegetation.
This desert is home to unique flora and fauna, such as the iconic Joshua Trees and the critically endangered Mexican Prairie Dog. It is also known for its impressive canyons, including the Copper Canyon, a series of canyons that rivals the size of the Grand Canyon in the United States.
The Chihuahuan Desert is a remarkable ecosystem that presents both challenges and opportunities for the species that have evolved to survive in this arid environment.
The Bolsón de Mapimí
Another desert region within Chihuahua is the Bolsón de Mapimí, which expands into the northern states of Durango and Coahuila as well. This sandy desert, known for its dune fields, covers an area of approximately 40,000 square miles (100,000 square kilometers).
The Bolsón de Mapimí is characterized by extreme heat during the summer, averaging temperatures above 100 degrees Fahrenheit (37.8 degrees Celsius). The scarce rainfall received in this desert is crucial for the survival of the unique vegetation, which includes various species of cacti and desert shrubs.
Despite its harsh conditions, the Bolsón de Mapimí is home to a variety of animal species, including the desert kit fox, desert bighorn sheep, and several bird species adapted to the arid environment.
The Samalayuca Dune Fields
Located in the southern part of Chihuahua, the Samalayuca Dune Fields are a fascinating desert region that features extensive sand dunes spanning an area of approximately 125 square miles (320 square kilometers). These dunes, formed by wind erosion over thousands of years, can reach heights of up to 150 feet (46 meters).
The sandy and arid conditions make the Samalayuca Dune Fields a challenging habitat for most organisms. However, it is home to unique plant species, such as the Yucca elata, commonly known as the “soaptree yucca.” The dune fields also harbor various small animal species, including reptiles and insects adapted to the desert environment.
The Samalayuca Dune Fields attract visitors, particularly those interested in sandboarding and off-road adventures, making it a popular destination for outdoor enthusiasts.
The Unique Ecology of Chihuahua’s Deserts
The desert regions within Chihuahua exhibit a distinct ecology shaped by extreme heat, limited water availability, and other desert-specific conditions. These ecosystems have managed to sustain a diverse range of specialized plant and animal species that have adapted to survive in such harsh landscapes.
While arid deserts make up only a portion of Chihuahua, they contribute to the state’s natural heritage and attract research, tourism, and outdoor activities. The unique ecology of these deserts provides valuable insights into the resilience of life in extreme environments and underscores the importance of conserving and understanding these fragile ecosystems.
Chihuahua: Beyond the Deserts
Now that we have explored the desert regions of Chihuahua, it is essential to highlight the state’s diverse natural features that extend beyond the arid landscapes. Chihuahua boasts a range of geographical and ecological wonders, offering a wealth of opportunities for exploration and appreciation.
The Sierra Madre Occidental
The Sierra Madre Occidental, a prominent mountain range that runs through Chihuahua, plays a vital role in the state’s geography and biodiversity. It is one of the longest mountain ranges in Mexico and hosts a variety of ecosystems due to its significant altitudinal variation.
From lush pine forests in the higher elevations to oak woodlands and grasslands in lower regions, the Sierra Madre Occidental supports a diverse range of plant and animal species. It is also home to the Copper Canyon system, a network of awe-inspiring canyons deeper than the Grand Canyon.
Exploring the Sierra Madre Occidental allows visitors to experience Chihuahua’s natural beauty beyond the desert landscapes and appreciate the rich biodiversity found within the state.
The Basaseachi Waterfall
Chihuahua is also home to the Basaseachi Waterfall, a magnificent natural wonder located within the Copper Canyon system. With a height of approximately 807 feet (246 meters), Basaseachi is one of the highest waterfalls in Mexico.
Surrounded by lush vegetation and dramatic cliffs, the waterfall offers a breathtaking sight and attracts nature enthusiasts, hikers, and photographers. The surrounding area provides a serene setting for outdoor activities, such as camping and birdwatching, allowing visitors to immerse themselves in Chihuahua’s diverse natural landscape.
The Cumbres de Majalca National Park
Located near the state capital, Chihuahua City, the Cumbres de Majalca National Park offers a scenic escape from urban life. The park encompasses a mountain range and pine forests, providing opportunities for hiking, camping, and wildlife spotting.
Within the park, visitors can explore various trails, enjoy panoramic views from elevated vantage points, and encounter a range of local flora and fauna. The park’s tranquil setting serves as a reminder of the diverse natural beauty that Chihuahua has to offer beyond its desert regions.
Discovering Chihuahua’s Rich Natural Heritage
Chihuahua’s natural heritage extends far beyond its desert regions, offering a tapestry of geographical features, ecosystems, and breathtaking attractions. From the majestic mountain ranges to the cascading waterfalls and national parks, the state invites exploration and appreciation of its diverse natural landscapes.
Whether you find yourself captivated by the arid deserts or enchanted by the verdant mountains, Chihuahua’s unique beauty and ecological wonders promise an unforgettable experience.
The Importance of Environmental Preservation
As we have explored the geographical and ecological aspects of Chihuahua, it becomes evident that the preservation of these natural landscapes is of utmost importance. The delicate balance between desert ecosystems, mountain ranges, and other habitats must be safeguarded to ensure the continued existence of unique wildlife and diverse flora.
Additionally, promoting sustainable tourism practices and raising awareness about the significance of conserving natural resources are crucial for the long-term well-being of Chihuahua’s environment. By embracing responsible practices and supporting conservation efforts, we can contribute to the preservation of Chihuahua’s natural heritage for future generations to enjoy.
Let us appreciate the wonders of Chihuahua, from its desert regions to its mountain peaks, and strive to protect and cherish these remarkable landscapes.
Key Takeaways: Is Chihuahua a Desert?
- Chihuahua is not a desert but a state in Mexico.
- Chihuahua does have desert regions, like the Chihuahuan Desert.
- The Chihuahuan Desert is the largest desert in North America.
- Chihuahua is known for its diverse landscapes, including mountains and canyons.
- Chihuahua is home to the Copper Canyon, also known as Barrancas del Cobre.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are you curious about the Chihuahua desert? Here are some commonly asked questions to satisfy your curiosity:
1. How did the Chihuahuan Desert get its name?
The Chihuahuan Desert is named after the Mexican state of Chihuahua, where a significant portion of the desert is located. It covers parts of northern Mexico and southwestern United States, making it the largest desert in North America. The desert landscape is characterized by its unique flora and fauna, adapted to survive the extreme desert conditions.
The Chihuahuan Desert is known for its diverse ecosystems, including grasslands, shrublands, and desert scrub. It is home to a variety of plant and animal species, some of which are found nowhere else in the world.
2. What is the climate like in the Chihuahuan Desert?
The climate in the Chihuahuan Desert can vary greatly depending on the location and elevation. Generally, the desert experiences hot summers and mild winters. It receives low precipitation throughout the year, with most rainfall occurring during the summer months as thunderstorms.
Due to its diverse topography, the Chihuahuan Desert can have significant temperature variations between different areas. The higher elevations tend to be cooler, while the lower elevations experience scorching heat. The desert’s climate presents a challenging environment for both plants and animals to adapt and survive.
3. What kind of wildlife can be found in the Chihuahuan Desert?
The Chihuahuan Desert is home to a wide range of wildlife, including mammals, reptiles, birds, and insects. Some of the iconic animals found in the desert include the roadrunner, desert tortoise, coyote, and kangaroo rat. The desert is also an important habitat for migratory birds, providing nesting grounds and stopping points during their long journeys.
In addition to these animals, the Chihuahuan Desert is known for its unique plant life, such as cacti, yuccas, and agaves. These plants have adapted to survive the harsh desert conditions, often with specialized features like spines or water-storing capabilities.
4. Can you visit the Chihuahuan Desert?
Absolutely! The Chihuahuan Desert offers opportunities for visitors to explore and appreciate its unique beauty and biodiversity. There are several national parks, state parks, and nature reserves that provide access to the desert’s different ecosystems and recreational activities. Visitors can hike, camp, bird-watch, or simply enjoy the stunning scenery of this remarkable desert.
However, it is essential to keep in mind that the desert can be a harsh environment. It’s crucial to come prepared with plenty of water, sun protection, and appropriate clothing. It’s also important to respect the fragile ecosystem and adhere to any park regulations to preserve the desert’s natural wonders for future generations.
5. What is the economic significance of the Chihuahuan Desert?
The Chihuahuan Desert plays a significant role in the region’s economy. Agriculture, ranching, and mining are important industries in areas where the desert is located. The desert’s soils are often rich in minerals, making it a valuable resource for mining operations.
Furthermore, tourism related to the desert’s natural attractions contributes to the local economy. Visitors come to explore the unique landscapes, wildlife, and cultural heritage of the Chihuahuan Desert, providing economic opportunities for local communities. The desert’s biodiversity also attracts researchers and scientists from around the world, further boosting the region’s economy through scientific exploration and study.

The Chihuahuan Desert: Our North American Outback
In conclusion, it is important to wrap up our discussion by summarizing the key points. First, we talked about the importance of using a conversational tone with simple language when writing for a 13-year-old reader. This helps to ensure clarity and understanding. Secondly, we emphasized the need to avoid jargon and use concise sentences with no more than 15 words. This keeps the information easy to digest and prevents confusion. By adhering to these guidelines, we can effectively communicate our message in a professional and reader-friendly manner.
To recap, the main takeaways are: using a conversational tone, keeping the language simple, avoiding jargon, and writing concise sentences. These tips will help engage and inform a 13-year-old reader. By using these techniques, we can craft professional and accessible content that effectively conveys our message.
